Determination of the thermal stability (Tm) of proteins using nanoDSF

BioDevCenter
Senior Principal Scientist
Thermal stability is an important parameter in the selection of suitable enzymes, antibodies or other biotechnologically produced proteins for industrial or pharmaceutical applications. The NMI offers the determination of the protein "melting point" Tm in the screening process. For this purpose, nanoDSF technology is used, which is based on changes in tryptophan fluorescence depending on the molecular environment.
Correct three-dimensional folding is essential for the biological function of proteins as catalysts or as binding partners for other molecules.
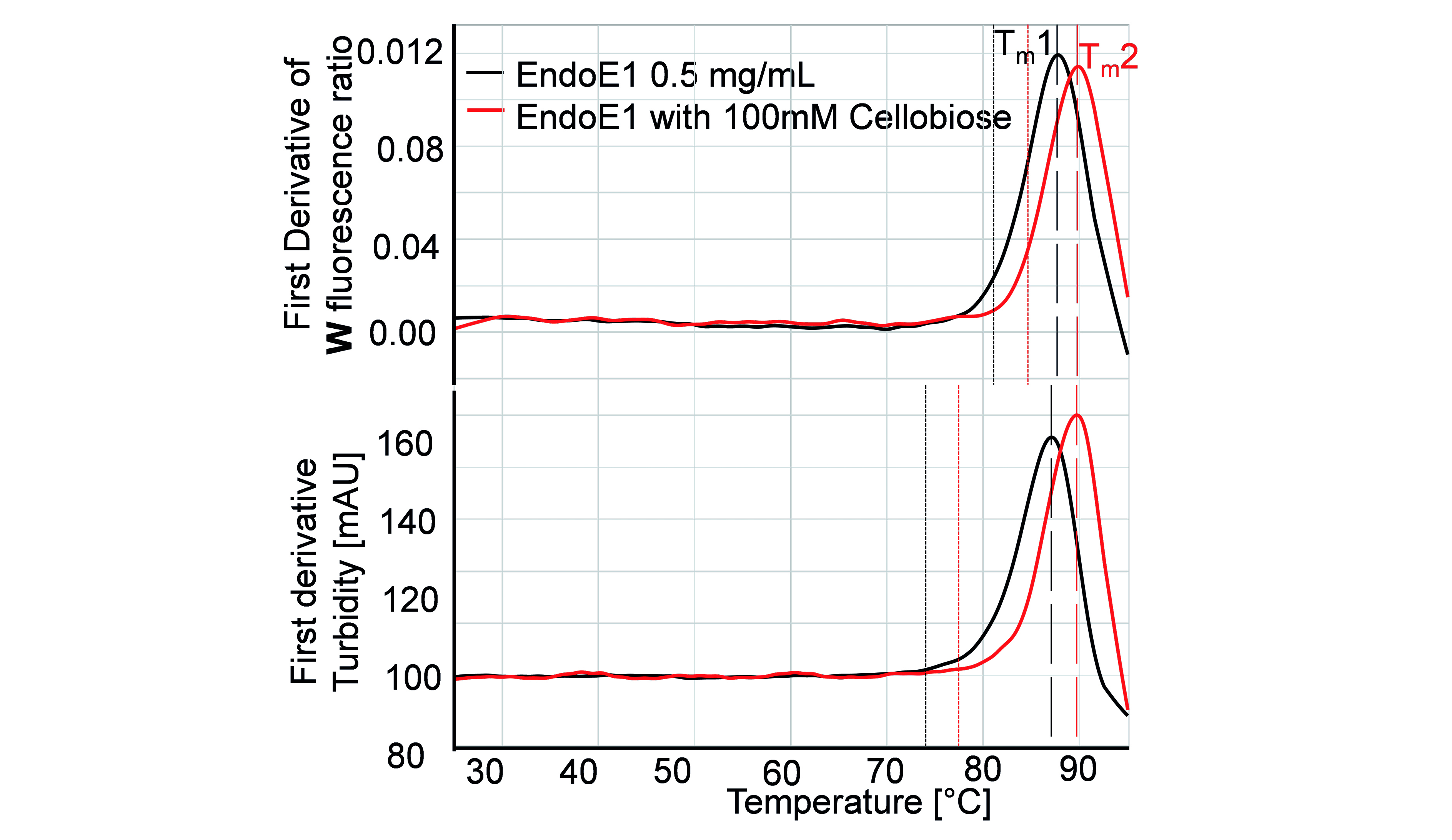
The stability of the three-dimensional arrangement is an intrinsic molecular property. It depends on intramolecular bonds and interactions, such as disulfide bridges, ionic or hydrogen bonds, on the primary sequence of amino acids and on the type of post-translational modifications, such as glycosylations. If there are several candidates for a target product profile or increased requirements for thermal stability, nanoDSF can be used in the screening process to determine the most suitable candidate quickly and with little material requirement.
However, the three-dimensional stability is also dependent on environmental conditions such as pH value and buffer composition or the presence of other molecules such as binding partners, solvents or chaotropic reagents. Using nanoDSF, different formulations can be tested at the NMI for a specific target molecule and thus, for example, optimal storage buffers, reaction conditions or resistance to destabilizing conditions can be found.
We would be happy to create a customized offer for you!
Here you will find interesting posters on this service with further information:
Analytical Characterization of Commercial Recombinant Endoglucanase E1, Optimizing reaction conditions for deglycosylation of intact proteins using a novel enzyme PNGase Rc